17.07.2025 by Viktor Siebert
MDS-C1-CV-75 Power Supply with Intermittent Error: A Case from the Netherlands
A long-standing customer from the Netherlands sent us the Mitsubishi power supply MDS-C1-CV-75 for inspection. The machine had recently started to show intermittent startup issues: sometimes the unit worked immediately, sometimes it displayed error code Alarm 9, indicating an internal voltage fault.
Troubleshooting with Many Suspicions
The customer operates several identical machines in his production facility, all of which have been running reliably for many years. This error was new to him and initially unclear. Even more confusing: the connected modules such as the spindle unit and servo amplifiers occasionally showed various fault messages.
His maintenance technician first suspected an issue with one of the axis amplifiers. Later he replaced the spindle module mwithout success. Only after swapping all modules (luckily he had several identical machines to work with), it became clear: the problem originated in the power supply itself.
In-Depth Diagnostics in Our Repair Facility
Once the power supply arrived at our workshop, we performed a thorough initial inspection. At first, the unit showed no noticeable problems, it didn’t react to simple load tests or mechanical vibration. But our experienced technicians are very familiar with the typical failure patterns and subtle clues, like smell.
Upon opening the unit, a characteristic odor, well known to electronics specialists, was noticeable: the smell of leaked electrolyte from aged aluminum electrolytic capacitors (electrolytic caps).
Why Do Electrolytic Capacitors Leak? A Technical Explanation
Electrolytic capacitors are made up of aluminum foil, a water-based electrolyte, a separator, and a sealing system. Over time, due to thermal stress, electrical aging, humidity, or manufacturing defects, the following can occur:
- The capacitor’s seal fails
- The electrolyte evaporates, leaks out, or penetrates the PCB
- This leads to corrosion and leakage currents, ultimately causing short circuits
This is particularly critical in CNC power supplies that operate under high thermal load and variable environmental conditions (temperature, humidity). The leaked electrolyte is conductive and corrosive, damages PCB traces, and causes errors that are difficult to reproduce.
Damage Caused by Leaked Electrolyte
In this case, several capacitors in the internal power supply section had leaked. The electrolyte had penetrated the circuit board, damaged traces, and caused short circuits. These short circuits only occurred depending on temperature and humidity which explained the customer’s irregular error pattern.
Our Standardized Preventive Overhaul
The power supply was subjected to a complete and standardized overhaul in our facility. This included:
- Full disassembly of the unit
- Replacement of all performance-relevant and aging components, especially electrolytic caps, power resistors, and relays
- Special cleaning of the board, with all electrolyte residues removed under a microscope
- Repair or replacement of damaged PCB traces
- Inspection and, if needed, renewal of all thermal connections
- Preventive replacement of fans and thermal sensors
Our Detailed Testing Procedure
After the overhaul, each unit undergoes a multi-stage testing process:
- Initial cold-start test
- Machine load simulation over several hours
- Cyclic on/off testing to analyze startup behavior
- Final test under full machine operation conditions with connected axis modules on our in-house test station
All results are recorded and stored in our digital test protocol. The unit is only released when all criteria are met.
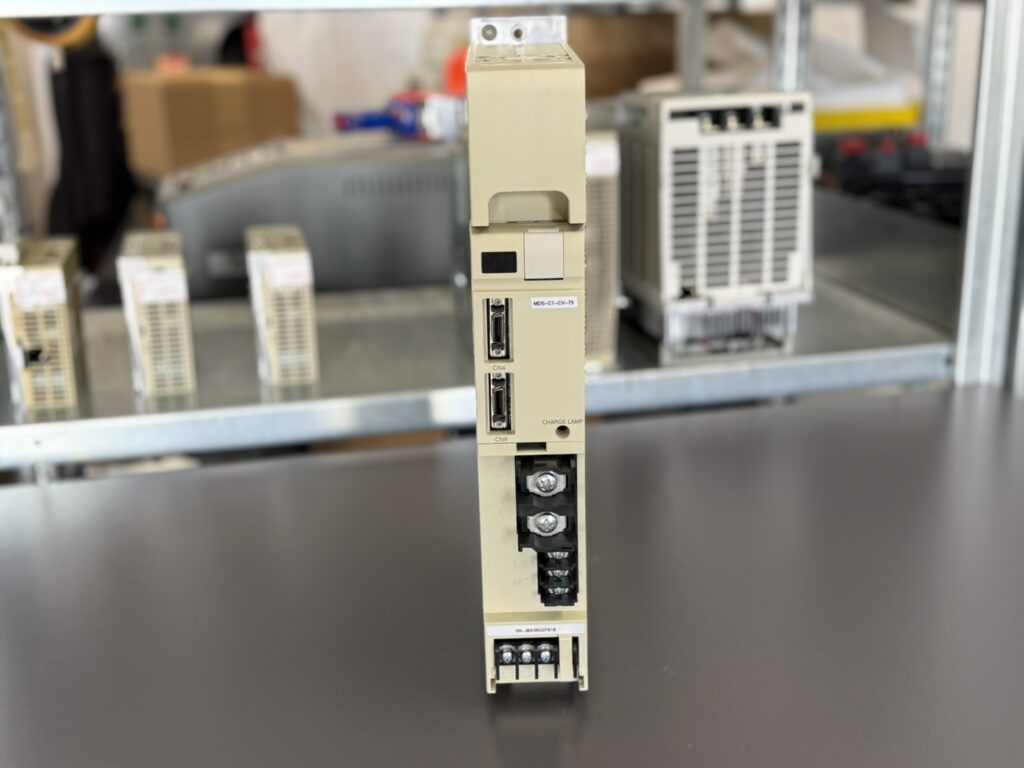





To mentioned Mitsubishi Power Supply: Mitsubishi MDS-C1-CV-75 Power Supply
More details about our Mitsubishi repair services can be found here:
Mitsubishi drive Repair by Industrypart
📞 Feel free to contact us with any questions about your Mitsubishi drive technology.
Our expert team is happy to help!
Technical Summary of the Unit
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Type | MDS-C1-CV-75 |
| Power Output | 7.5 kW |
| Input | 3PH 200/200–230 V, 50/60 Hz, 26 A |
| Auxiliary Input | 1PH 200/200–230 V, 50/60 Hz, 0.2 A |
| Output | DC 270–311 V, 30 A |
| Manual Reference | BNP-C3000 |
| Weight | approx. 7 kg |
Operating Environment & Connected Equipment
The MDS-C1-CV-75 is part of the MELDAS MDS-C1 servo/spindle drive system by Mitsubishi Electric. It is typically used in:
- CNC machining centers
- CNC lathes
- Machines by Mazak, DMG MORI, Leadwell, Feeler, Victor Taichung
- Connected to:
- MDS-C1-V1/V2 servo drive units
- MDS-C1-SP spindle drives
- HA, HC, HC-R, HA-LF servo motors
Functional Description
The MDS-C1-CV-75 serves as the main power supply unit for servo and spindle drive systems. It:
- Converts 3-phase AC into stable DC bus voltage (270–311 V DC)
- Powers the servo and spindle amplifiers
- Handles energy recovery and safety shutdown functions
- Integrates overcurrent, voltage, and thermal protection
Alarms and Troubleshooting
| Alarm No. | Description | Cause | Remedy |
|---|
| 9 | Power Supply Alarm | Internal fault in power circuit | Check and possibly replace power unit |
| 50 | Overload 1 | Motor current exceeded limit (e.g. mechanical blockage) | Check load/motor, inspect parameters |
| 70 | Spindle Communication Error | Comm error between spindle drive and control | Check cable, settings, grounding |
| 17 | A/D Converter Error | Fault in A/D converter circuit | Replace or inspect electronics |
| 32 | Power Module Error (Overcurrent) | Overcurrent or failure in IGBT power module | Check for short circuits, inspect module |
Internal PCB Designations
| Component Type | PCB Part Number(s) | Qty |
|---|
| Control Board | RK415D-2 or BN638A309G51 | 1 |
| Power Board | RK481B-75 or BN638A104G51A | 1 |
| Heatsink (no power stage) | Referred to as “Power Section” | 1 |