21.09.2025 by Viktor Siebert
Overheating, Shutdown, Total Failure: The Case of a Mitsubishi MDS-C1-V1-45 Servo Drive Unit
It often starts with something seemingly minor: a warning message on the machine display that appears more and more frequently. In this case, it was a Mitsubishi MDS-C1-V1-45 Servo Drive Unit installed in a heavily used machine tool. Increasingly, the message “Overheating” appeared. For the operator, this was initially just an inconvenience the machine could still be operated temporarily, as long as the protection circuits intervened and the drive did not shut down completely.
To resolve the problem, the customer decided to have the fans replaced. The electrician in charge used aftermarket parts ordered online. While they looked similar and fit mechanically, they did not meet the required specifications. Airflow, thermal resistance, and bearing quality all differed significantly from the original components.
The result was predictable: cooling remained insufficient. The drive continued to overheat, and the thermal load on the power semiconductors steadily increased. Eventually, the stress reached a critical point: the transistor modules (IPM) burned out. From that moment on, the machine was no longer operational instead, it produced a cascade of alarm messages. Further operation was impossible. At the same time, parts of the control board were also damaged by the heat.
The repair at industrypart GmbH
When the unit arrived at our workshop, the damage was obvious: heavily discolored and burned power modules, clear thermal marks on the circuit boards, and a compromised control section. We decided to carry out a complete overhaul and initiated our repair process.
The detailed procedure:
- Disassembly and cleaning The device was fully dismantled. Soot, dust, and thermal deposits were removed. Circuit boards were cleaned in an ultrasonic bath and then dried in an oven to eliminate residual moisture.
- Analysis and measurement Each assembly was checked individually. Defective power modules, overheated optocouplers, and damaged PCB traces were identified.
- Replacement of key components New original IGBT modules were installed, affected control ICs were replaced, and damaged PCB areas were repaired.
- Fan replacement This time, only genuine Mitsubishi fans were used, providing the exact airflow and temperature characteristics specified by the manufacturer.
- Preventive replacement To ensure long-term reliability, we also replaced electrolytic capacitors, optocouplers, and temperature sensors.
- Testing phase After the repair, the unit underwent an extensive testing program:
- Load testing under nominal operating conditions
- Continuous temperature monitoring during extended operation
- Signal verification on all control lines
- A 24-hour endurance run on our dedicated test bench
The outcome: the drive once again operated stably, cooling functioned properly, and all protective mechanisms performed as intended. The customer was able to reinstall the unit into their machine and continue production without further issues.
The message
This case clearly demonstrates: cheap spare parts and so-called quick fixes cause major damage in the long run. A fan costing only a few euros led here to the failure of critical components and a complete machine stoppage.
Prevention for the future
That is why we always recommend the following measures to our customers:
- Clean heat sinks and fans regularly (at least once a year).
- Only use approved original parts or replacements that meet the exact specifications.
- Replace electrolytic capacitors preventively every 7–10 years.
- Inspect connectors and cables regularly and replace them if worn.
A Mitsubishi MDS-C1-V1-45 is designed for a long service life – but only if maintenance and spare part management are carried out properly. With the right preventive measures, unplanned downtime and high consequential costs can be avoided.
Conclusion
The story of this defective drive highlights the importance of taking warning signals seriously and relying on quality. Preventive maintenance saves costs, protects machines, and ensures stable and predictable production.


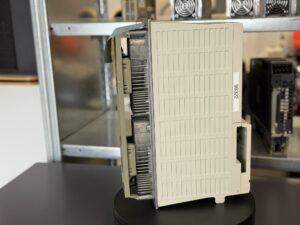



To mentioned Mitsubishi Drive: Mitsubishi MDS-C1-V1-45 Power Supply Unit
More details about our Mitsubishi repair services can be found here:
Mitsubishi drive Repair by Industrypart
📞 Feel free to contact us with any questions about your Mitsubishi drive technology.
Our expert team is happy to help!
Technical Summary of the Unit
| Feature | Value (according to nameplate) |
|---|
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Japan |
| Device Type | Servo Drive Unit |
| Model | MDS-C1-V1-45 |
| Rated Power | 4.5 kW |
| Input Supply (DC bus) | 270–311 V DC, 20 A |
| Control Supply (AC) | 220–230 V AC, 1-phase, 0.2 A, 50/60 Hz |
| Output | 3-phase 158 V AC, 0–240 Hz, 28 A |
| Software ID | S/W ENDS62W00A8 |
| Hardware Version | H/W VER. H |
| Manual Reference | BNP-62000 |
| Code | EMS0178 |
| Cooling | Fan cooling (typical, approx.) |
| Dimensions | approx. 350 × 120 × 300 mm |
| Weight | approx. 8–10 kg |
| Protection Class | approx. IP20 |
Application Environment & Compatible Devices
- Typical machines: CNC machining centers, lathes, milling machines (e.g. Mazak).
- Compatible controllers: Mitsubishi CNC C1 series controllers, Mazak controllers.
- Compatible motors: Mitsubishi AC servo motors of the HF and SJ series.
- Applications: High-precision axis control, feed axes, spindle drives in machine tools.
Functional Description
The MDS-C1-V1-45 Servo Drive Unit controls Mitsubishi AC servo motors.
Main tasks:
- Current and torque control.
- Communication with the CNC controller.
- Feedback via encoder for accurate positioning.
- Protection mechanisms: overcurrent, overheating, overvoltage, communication errors.
- Efficiency: optimized power electronics for reliable machine operation.
Alarm Messages & Troubleshooting
| Code | Error Description | Cause | Solution |
|---|
| 12 | Memory error | Fault in memory IC | Replace drive |
| 17 | A/D converter error | Failure in A/D converter | Check/replace control board |
| 21 | No signal (UVW, encoder) | Cable/connector defect | Inspect cable, check motor |
| 25 | Absolute position lost | Battery empty or cable defect | Replace battery, check cable |
| 27 | CPU error in absolute detector | Hardware defect | Check/replace board |
| 32 | Power module overcurrent (IPM) | Overheating, wrong fan, defect | Replace fan, check module |
| 42 | Feedback error 1 | Encoder failure | Inspect/replace encoder |
| 46 | Motor overheating | Fan failure, blockage | Replace fan, clean unit |
| 50 | Overload 1 | Overcurrent > rated | Inspect load, improve cooling |
| 58 | Collision detected | Mechanical resistance | Inspect machine axis |
Components
| Type | Designation | Qty |
|---|
| Control board | RK112A-21 or BN634A980G51 B | 1 |
| Power board | RL125B-V1-90 or BN638A163G51 / RL122B-V1 or BN638A153G51 A | 1 |
| Power module | BKO-NC1206 H92 MP03-V1-45
BKO-NC1207 H90 A2-V1-45 | 1 |
| Heat sink | Aluminum with fan | 1 |
| Fan module | Axial fan 24 V | 1 |
| Connectors | Power and signal connectors | several |