06.01.2026 by Viktor Siebert
Repair of a Mitsubishi MDS-B-V1-35 AC Servo Drive Unit. Cause: Fan failure and thermal damage to the power stage
The Mitsubishi MDS-B-V1-35 AC Servo Drive Unit was sent to us due to unstable machine behavior. The customer reported strong vibrations starting at approximately 700 revolutions per minute, which increased further with rising speed. After a short operating time, the drive shut down and reported an overload.
In practice, such symptoms are often initially attributed to the motor, mechanics, or parameter settings. In this case, however, the root cause was clearly located inside the drive itself and could have been avoided through simple preventive measures.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Electric |
| Type | MDS-B-V1-35 |
| Device type | AC Servo Drive Unit |
| Series | MDS-B |
| DC input voltage | approx. 270–311 V DC |
| AC input voltage | 200–230 V AC, 50/60 Hz |
| Input current | approx. 17 A |
| Output | 3-phase AC |
| Cooling | Forced air cooling via internal fan |
| Display | 7-segment LED |
| Installation | Control cabinet |
| Typical application | CNC axis drive |
Operating environment and typical applications
The MDS-B-V1-35 is used in CNC machine tools to control servo axes. Typical applications include feed axes in milling machines, lathes, and machining centers.
The unit is designed for installation in a control cabinet. A clean environment, proper ventilation, and sufficient airflow are essential, as the power stage continuously dissipates heat during operation.
Design and main assemblies
| Assembly | Designation | Function |
|---|
| Control board | RK111B-11 or BN634A815G51 D | Control, communication, protection functions |
| Power board | RK122B-V1-35 or BN634A813G51 B | Power stage, axis power supply |
| Power section | Integrated | Servo motor drive |
| Fan unit | Internal | Cooling of power semiconductors |
Condition on arrival
Already from the initial fault description, a typical thermal damage pattern was evident. The vibrations occurred reproducibly above a certain speed, which is a classic indication of unstable current control caused by temperature-dependent changes in electronic components.
After opening the unit, the cause became immediately clear. The internal cooling fan was completely blocked by dirt and deposits. The rotor was mechanically seized, meaning that no active cooling had taken place over an extended period.
As a result, the power stage was exposed to continuous overheating, which ultimately led to failure of the power semiconductors. The reported overload was therefore not the root cause, but rather a protective response to an already advanced internal defect.
Repair process
After disassembly, the unit was thoroughly cleaned. All heat sinks, air channels, and circuit boards were freed from dust and contamination. This was followed by a detailed electrical inspection of the power stage.
Due to the thermal damage, repair of the power stage was required. The blocked fan was replaced without exception, as reuse in such cases is not technically reasonable.
After completion of the repair, the servo drive was tested on a test bench under realistic load conditions. Particular attention was paid to behavior at higher speeds and to thermal stability. The unit then operated without vibration and showed stable control behavior across the entire speed range.



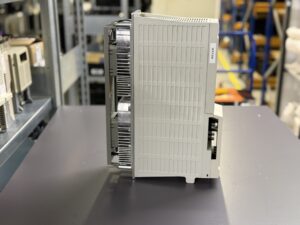




To mentioned Mitsubishi Drive: Mitsubishi Servo Drive Unit MDS-B-V1-35
More details about our Mitsubishi repair services can be found here:
Mitsubishi drive Repair by Industrypart
📞 Feel free to contact us with any questions about your Mitsubishi drive technology.
Our expert team is happy to help!
Typical alarms and troubleshooting for the MDS-B-V1-35
| Alarm code | Description | Cause | Corrective action |
|---|
| 32 | Power module overcurrent | Overcurrent in the power stage | Check motor and drive, repair power stage |
| 3A | Overcurrent | Mechanical blockage or unstable control | Check mechanics, verify parameters |
| 3B | Power module overheat | Insufficient cooling | Check fan and heat sinks |
| 45 | Fan stop | Fan failure or blockage | Clean or replace fan |
| 50 | Overload 1 | Continuous overload | Reduce load, check cooling |
| 51 | Overload 2 | High current over a longer period | Verify drive sizing |
| 46 | Motor overheat | Thermal overload | Check motor and drive cooling |
| A6 | Fan stop warning | Fan standstill detected | Immediate maintenance required |
Warnings and alarms related to fan failure and overheating should never be ignored. In many cases, they are the final indication before severe damage occurs.
Preventive maintenance as a key factor
This repair case clearly demonstrates that the actual trigger was not a complex electronic defect, but a missed maintenance task. A blocked fan is not a sudden failure, but a condition that develops over months or years.
Recommended preventive measures:
- Regular visual inspection of fans
- Cleaning of fans and heat sinks
- Replacement of aged or noisy fans
- Inspection of airflow inside the control cabinet
- Removal of dust, oil mist, and chips
- Thermal checks on older drive systems
Replacing a fan involves minimal effort compared to repairing a damaged power stage and effectively prevents costly repairs and unplanned machine downtime.
Conclusion
The Mitsubishi MDS-B-V1-35 AC Servo Drive Unit was successfully repaired. The damage to the power stage was clearly caused by a failed cooling fan. This case clearly highlights the importance of preventive maintenance for servo drives.
A functioning cooling system is not a minor detail, but a fundamental requirement for the service life and operational reliability of drive systems. Regular maintenance protects electronic components, ensures machine availability, and significantly reduces long-term costs.